Recent investigations into TP-Link routers by U.S. government agencies have highlighted significant cybersecurity risks associated with widely used network devices. This blog post delves into the technical aspects of these concerns and explores how Genians can effectively address these challenges.
The TP-Link Security Dilemma: A Technical Deep Dive
TP-Link, supplying about 65% of routers for American homes and small businesses, is facing scrutiny due to several critical security concerns:
- Backdoors and Remote Access: Potentials intentionally inserted backdoors in TP-Link router firmware could allow unauthorized access. This risk is particularly concerning as it could enable covert data exfiltration or remote command execution.
- Data Collection and Transmission: The possibility of routers collecting and transmitting user data to external servers raises significant privacy and national security concerns. This could involve packet inspection, DNS queries logging, or even deep packet inspection (DPI) techniques.
- Firmware Vulnerabilities: Known vulnerabilities in TP-Link router firmware present entry points for malicious actors. These could include buffer overflow vulnerabilities, command injection flaws, or weak default configurations.
- Network Infrastructure Threat: Given their widespread use, compromised TP-Link routers could be leveraged for large-scale DDoS attacks, data interception, or as pivot points for lateral movement within networks.
- Insecure Firmware Update Mechanisms: Vulnerabilities in the firmware update process could allow for malicious code injection. This might involve man-in-the-middle attacks during the update process or exploitation of insecure update channels.
- Weak Encryption and Security Protocols: Concerns about the strength of encryption methods and security protocols used in TP-Link routers could lead to data interception or unauthorized access. This might include the use of outdated protocols like WEP or weak implementations of WPA2.
The Insider Threat: Shadow IT in Focus
An often overlooked aspect is the insider threat, particularly in the context of “shadow IT.” Employees or contractors might unknowingly introduce vulnerable devices, including TP-Link routers, into corporate networks, especially in remote work scenarios. This creates significant blind spots in network security and complicates risk management efforts.
Mitigating Risks with NAC-driven ZTNA Solutions
To address these challenges, Genians can provide a comprehensive approach:
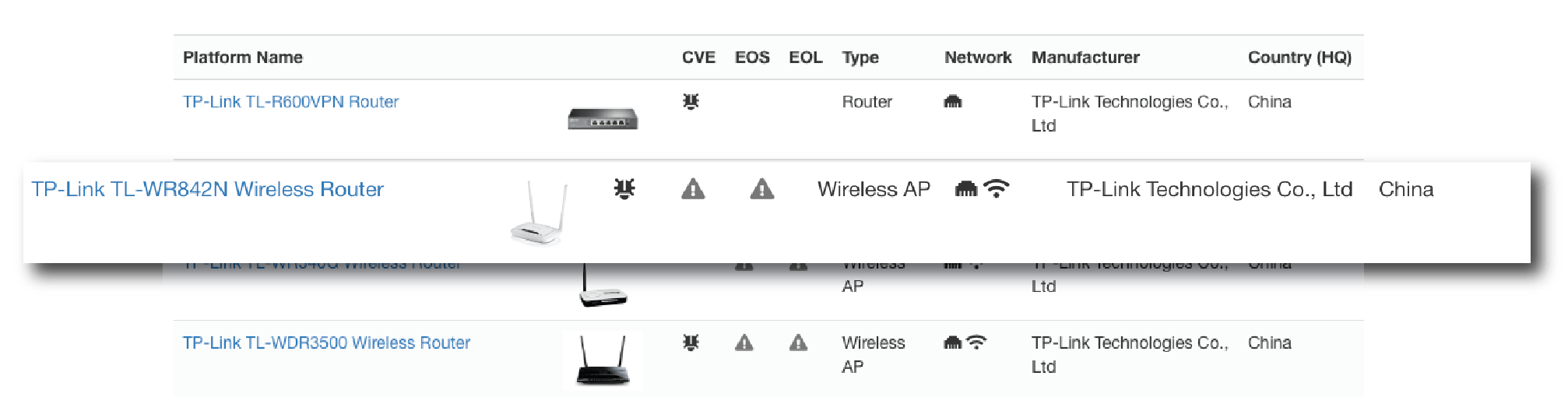
- Real-time Device Detection and Classification: Genians leverages Layer-2-based network sensing technology to detect and classify all IP-based devices on the network in real-time, including unauthorized TP-Link routers or those used by remote workers.
- Accurate identification of device platforms (e.g., “TP-Link TL-WR842N Wireless Router” instead of just “TP-Link Router”)
- Detection of unauthorized TP-Link routers or those used by unknown users.
- Continuous monitoring for new or changed devices on the network
- Micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement
- Detailed Device Information: Using Genians Device Platform Intelligence (DPI) technology, Genians can correlate crucial information about detected devices, including manufacturer details, End-of-Life (EoL) and End-of-Support (EoS) status, and known vulnerabilities (CVEs).
- Context-based Security Policy Enforcement: Based on the collected information, Genians can assess the risk level of each device and apply appropriate security measures according to organizational policies. This includes isolating unauthorized TP-Link devices,
- Zero Trust Approach: Genians’ NAC-driven Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) approach treats all devices as potential threats, requiring continuous authentication and authorization.
- Securing Remote Work Environments: The solution effectively manages TP-Link devices used by remote workers, enhancing the security of distributed work environments.
The ongoing investigations into TP-Link routers underscore the critical need for robust cybersecurity measures in our increasingly connected world. While government actions may lead to potential bans or restrictions, organizations must take proactive steps to secure their networks.
Genians’ comprehensive cybersecurity solutions empower CISOs, network managers, and security professionals to proactively address threats posed by devices like TP-Link and similar vulnerabilities. By strengthening network surveillance, enforcing strict security policies, and adopting a zero-trust approach, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture and defend against both internal and external threats.
Team Genians shares insights, stories, and updates on how we’re shaping the future of cybersecurity—one solution at a time.